|
A furnace is a device used for heating. The name derives from Latin fornax, oven. The earliest furnace was excavated at Balakot, a site of the Indus Valley Civilization, dating back to its mature phase (c. 2500-1900 BC). The furnace was most likely used for the manufacturing of ceramic objects. In American English and Canadian English, the term furnace on its own is generally used to describe household heating systems based on a central furnace (known either as a boiler or a heater in British English), and sometimes as a synonym for kiln, a device used in the production of ceramics. In British English the term furnace is used exclusively to mean industrial furnaces which are used for many things, such as the extraction of metal from ore (smelting) or in oil refineries and other chemical plants, for example as the heat source for fractional distillation columns. The term furnace can also refer to a direct fired heater, used in boiler applications in chemical industries or for providing heat to chemical reactions for processes like cracking, and is part of the standard English names for many metallurgical furnaces worldwide. The heat energy to fuel a furnace may be supplied directly by fuel combustion, by electricity such as the electric arc furnace, or through Induction heating in induction furnaces. A household furnace is a major appliance that is permanently installed to provide heat to an interior space through intermediary fluid movement, which may be air, steam, or hot water. The most common fuel source for modern furnaces in the United States is natural gas; other common fuel sources include LPG (liquefied petroleum gas), fuel oil, coal or wood. In some cases electrical resistance heating is used as the source of heat, especially where the cost of electricity is low. Combustion furnaces always need to be vented to the outside. Traditionally, this was through a chimney, which tends to expel heat along with the exhaust. Modern high-efficiency furnaces can be 98% efficient and operate without a chimney. The small amount of waste gas and heat are mechanically ventilated through a small tube through the side or roof of the house.
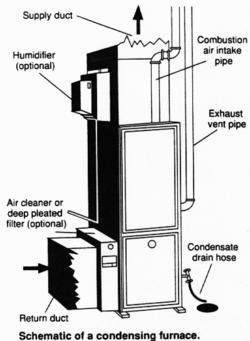
Modern household furnaces are classified as condensing or non-condensing based on their efficiency in extracting heat from the exhaust gases. Furnaces with efficiencies greater than approximately 89% extract so much heat from the exhaust that water vapor in the exhaust condenses; they are referred to as condensing furnaces. Such furnaces must be designed to avoid the corrosion that this highly acidic condensate might cause and may need to include a condensate pump to remove the accumulated water. Condensing furnaces can typically deliver heating savings of 20%-35% assuming the old furnace was in the 60% Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) range. In metallurgy, several specialised furnaces are used. These include:

The Manufacture of Iron -- Filling the Furnace, an 1873 wood engraving
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia : Manufacture of furnaces and burners |